Since the beginning of 2021, Window-M, the Russian optical-electronic complex, has recorded a significant increase in space activity in near-earth space, the Russian Ministry of Defense said.
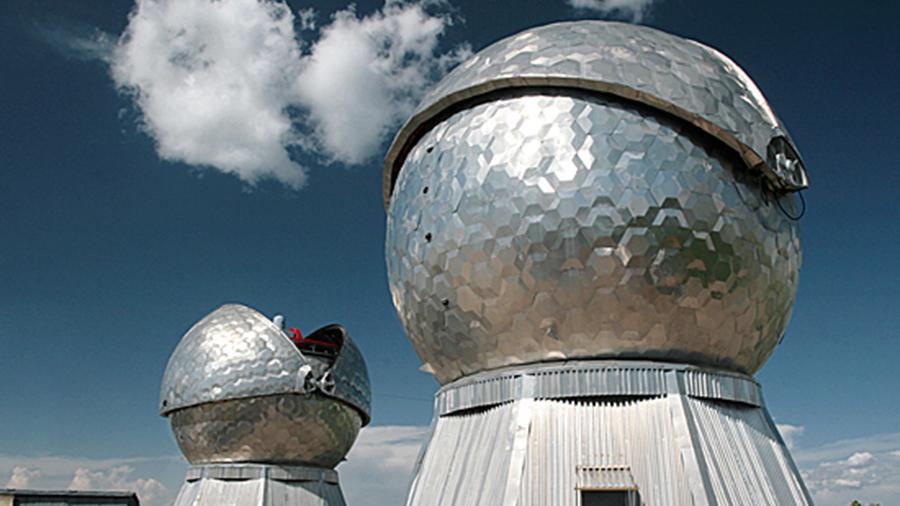
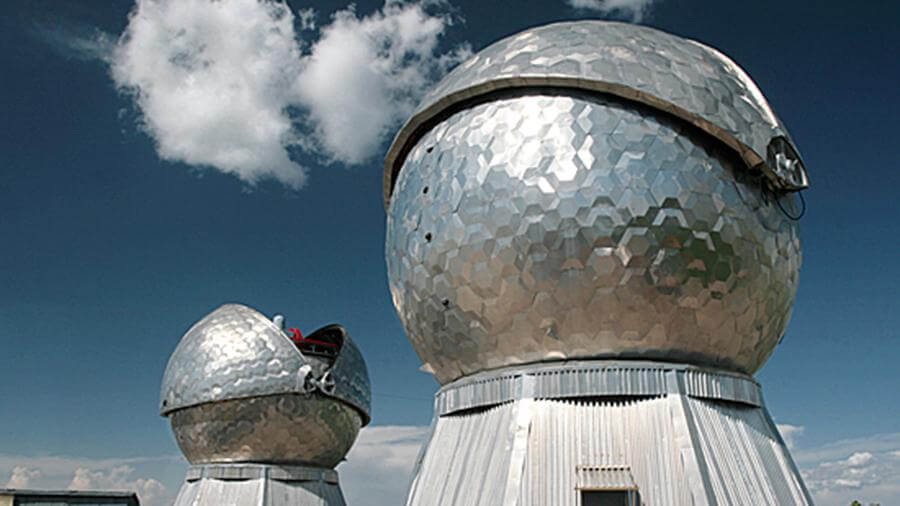
“Window-M, The Russian optical-electronic complex for the detection of space objects which is located in Tajikistan, in the Sanglok mountains (Pamir mountain system) and at an altitude of 2200 meters above sea level, detected movement of about 30,000 space objects for four months in 2021”, – the department reported.
A year earlier, “Window-M” detected more than 25 thousand space objects.
The Russian Ministry of Defense noted that “Window-M” is a special optoelectronic complex that allows monitoring space objects in orbits in the altitude range from 120 to 50 thousand kilometers from the Earth’s surface. It is noteworthy that at the maximum distance from the Earth’s surface, the “Window-M” complex can recognize an object the size of which does not exceed the size of a tennis ball.
“Window-M” was put on experimental combat duty back in 1999. A modernization was carried out in 2014 where it received the designation “Window-M”. Since 1999, the complex has carried out 12.5 million measurements of space objects, more than 7.5 thousand new high-orbit space objects were discovered, and about 800 spacecraft were controlled into working orbits.
It includes modern optoelectronic stations for detecting and collecting information about space objects, television detection equipment and new generation computing facilities, created on the basis of domestic element base.